Who is this guide for?
If you're looking to optimize your online content for Google Search, this guide is for you! Whether you're the owner of a growing business, the website owner of multiple sites, a DIY SEO expert, or an SEO specialist at a web agency, this guide will give you an overview of the best practices for improving your content's visibility on search engines. You won't find any secrets here that'll guarantee you a top spot on Google (sorry!), but following the best practices outlined in this guide will help you create a user-friendly website that search engines can crawl, index, and understand.
Optimizing your website for search engines involves making small modifications to certain parts of your website. While these changes may seem insignificant on their own, they can make a big difference when combined with other optimizations. You should build your website with the goal of providing a great user experience, and any optimization should be geared towards making that experience better. After all, one of the users of your website is a search engine, and it helps other users discover your content. SEO is about helping search engines understand and present your content in a way that's useful for users. Whether your website is large or small, the optimization topics in this guide apply to all sizes and types of sites. We hope this guide helps you create a website that users and search engines both love!
Getting Started
Glossary
This guide includes some important terms related to search engine optimization:
Index - The collection of web pages that Google knows about. When Google indexes a page, it reads the content and stores the URL of the page in its index.
Crawl - The process of looking for new or updated web pages. Google discovers URLs by following links, reading sitemaps, and other methods.
Crawler - An automated program that fetches web pages and adds them to the index.
Googlebot - The name of Google's crawler. Googlebot crawls the web continuously.
SEO - Search engine optimization. This refers to the process of making a website better for search engines and the job title of someone who does this professionally.
Are you on Google?
Check to see if your site is indexed by Google.
To check if your site is in Google's index, do a site search for your site's home URL. If results appear, your site is indexed by Google. For example, searching for "site:wikipedia.org" will return results, showing that Wikipedia is indexed by Google.
The site: operator does not guarantee that all URLs indexed under the prefix specified in the query will be returned. To learn more about how the site: operator works, please visit the Google Search Help page.
If your site isn't in Google
If Google misses a website, it could be due to several potential factors:
- Insufficient connections with other sites on the web
- A recently launched site that has not been crawled yet
- Inaccessible content as a result of complicated site design
- An error encountered by the crawler
- Blocked access due to a website policy.
- How do I get my site on Google?
How do I get my site on Google?
Google Search is an automated system that uses web crawlers to explore the internet, looking for websites to add to its index. Most sites listed in the results are found and added automatically without manual submission. Learn how Google discovers, crawls, and displays webpages.
The Search Essentials offer the most essential elements of constructing a website that is friendly with Google. Although there is no guarantee that their crawlers will spot a particular website, following the Search Essentials will assist in making your website visible in the search results.
Google Search Console provides tools to help you submit your content to Google and track your progress in Google Search. Search Console can also send you alerts in case Google encounters any issues with your website. Sign up for Search Console to make use of this service.
Here are a few basic questions to ask yourself about your website when you get started.
- Have I optimized my website for Google?
- Am I providing useful, high-quality content to visitors?
- Is my local business visible on Google searches?
- Is my website content accessible on all types of devices quickly and easily?
- Is my website secure and up to date on security measures?
Do you need an SEO expert?
If you want to increase your visibility on search engines, you may want to hire an SEO expert. An SEO specialist is someone with the knowledge and experience to optimize your website. This guide will provide you with the necessary information to get started. Additionally, a professional SEO expert can review your pages and make further improvements.
When considering the potential benefits of hiring an SEO, it is important to weigh up the pros and cons before making a decision. A reputable SEO can bring great improvements to your website and save time, while an irresponsible SEO can cause irreparable damage. There are many services provided by SEOs, agencies and consultants that are beneficial to website owners, such as:
- Review of website architecture and content
- Technical advice on website hosting, redirects, error pages, and JavaScript implementation
- Content creation and optimization
- Strategic development of online business campaigns- Keyword analysis and optimization
- SEO training and guidance
- Specialized knowledge of specific markets and regions
Before beginning your search for an SEO, it's advisable to become familiar with search engine fundamentals. To do so, we suggest going through this guide, as well as the following resources:
Strategies for optimizing websites for Google
1. Tips on selecting an SEO professional
2.Overview of Google's web crawling, indexing and serving process
Hiring an SEO early on is beneficial when planning a website redesign or launching a new site, as they can ensure that the site is set up with search engine optimization in mind. Even with an existing website, an SEO can help optimize it to help it rank better. To learn more about when to hire an SEO and what to look for, read the article Do You Need an SEO.
Help Google find your content
To ensure that Google can find your website, the first step is to submit a sitemap. A sitemap is a file that informs search engines about any new or modified pages on your site. For more information on how to build and submit a sitemap, please refer to the corresponding guide.
Additionally, Google discovers pages via links from other sites. To encourage people to discover your website, be sure to promote it.
Tell Google which pages you don't want crawled
Implement robots.txt to prevent unwanted crawling of non-sensitive information.
A robots.txt file is a way of telling search engines which parts of your site they are allowed to access and crawl. This file is placed in the root directory of your website and must be named robots.txt. It is possible, however, for pages blocked by robots.txt to still be crawled, so for any sensitive pages, it is recommended to use a more secure method.
#brandonsbaseballcards.com/robots.txt
#Tell Google not to crawl any URLs in the shopping cart or images in the icons folder,
#because they won't be useful in Google Search results.
User-agent: googlebot
Disallow: /checkout/
Disallow: /icons/You may not want certain pages of your website to be crawled by search engine bots. This is because these pages may not be useful to users if found in the search results. If your website uses subdomains and you would like to prevent certain pages from being crawled on a particular subdomain, you must create a separate robots.txt file for this subdomain. For more information on how to use robots.txt files, please refer to this guide.
Read about several other ways to prevent content from appearing in search results.
- Refrain from permitting Google to crawl your internal search result pages. Users may become frustrated when they click a search engine result and find themselves on another search result page within your website.
- Block any URLs generated by proxy services from being crawled.
For sensitive information, use more secure methods
Using a robots.txt file is not an adequate or effective way to protect sensitive or confidential material. It will not stop your server from delivering those pages to a browser that requests them, as search engines may still be able to access the URLs you block and display their URLs without a title link or snippet. Moreover, rogue search engines that do not follow the Robots Exclusion Standard could ignore the directions of your robots.txt. Additionally, a user could try to guess the URL of the content you do not want them to see by inspecting the directories or subdirectories in your robots.txt.
If you only want to keep the page from appearing in Google, put a noindex tag on it. For more secure protection, utilize authorization methods like requiring a password or taking the page off your website entirely.
Help Google (and users) understand your content
Let Google see your page the same way a user does
Googlebot should be able to view a page in the same way that an average user does. To ensure optimal rendering and indexing, always give Google access to the JavaScript, CSS, and image files used by your website. If your site's robots.txt file prevents the crawling of these assets, it can negatively affect the performance of our algorithms when rendering and indexing your content, resulting in lower rankings.
The URL Inspection tool is the best way to understand how Google perceives and displays your content. You can utilize it to identify and solve numerous indexing problems on your website.
Create unique, accurate page titles
The <title> element should be placed in the <head> element of the HTML document in order to provide both users and search engines with information about the topic of the particular page. It is important to create unique title text for each page on the website in order to ensure maximum visibility.
<html>
<head>
<title>My Online Bookstore - Find Your Favorite Books Here</title>
<meta name="description" content="My Online Bookstore provides a wide range of books, from classic literature to contemporary bestsellers. We offer competitive prices and a user-friendly shopping experience.">
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>Influencing your title links and snippets in search results
In the event that your webpage is displayed on a search results page, the text inside the <title> tag could be used as the clickable link for the search result. This means that it's important to choose a descriptive and concise title that accurately reflects the content of your page. For those who are unfamiliar with the components of a Google search result, a helpful resource is the "anatomy of a search result" video by Google, which can be found at this link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vS1Mw1Adrk0&ab_channel=Google.

Your website's homepage <title> element can feature the name of your business or website, and may also include essential details such as the business's location or its primary products or services.
✅ Accurately describe the page's content
Select a title text that sounds natural and effectively conveys the subject matter of the page's content.
🚫 Avoid :
- Using title text that is unrelated to the page's content, or default and vague text such as "Untitled" or "New Page 1."
✅ Create unique <title> elements for each page
Ensure that every page on your website has a distinctive text in the <title> tag to aid Google in identifying how that page is different from the rest of the pages on your site. If your website has separate mobile pages, make sure to include descriptive text in the <title> tags of the mobile versions as well.
🚫 Avoid :
- Use a uniform title across your website's pages or a significant number of pages by implementing a single
<title>element.
✅ Use brief, but descriptive <title> elements
The <title> element can convey information succinctly or in detail. However, if the content in the <title> tag exceeds an optimal length or is deemed less pertinent, Google might display a truncated version of the text or a title link that's auto-generated in the search outcome.
🚫 Avoid :
- It's unhelpful to users when
<title>elements contain overly long text. - Including unnecessary keywords in your
<title>element is a form of keyword stuffing.
Use the meta description tag
The meta description tag of a webpage provides a brief overview of the webpage's content to search engines such as Google. While a page's title can be concise, the meta description tag can span a sentence or two, or even a brief paragraph. The meta description tag, like the <title> element, is positioned within the <head> element of the HTML document.
<html>
<head>
<title>The Gourmet Kitchen - Cooking Tips, Recipes, and Product Reviews</title>
<meta name="description" content="The Gourmet Kitchen is your go-to source for all things cooking. From easy-to-follow recipes to in-depth product reviews, we've got you covered. Whether you're a beginner or a seasoned pro, our cooking tips and advice will help you take your culinary skills to the next level.">
</head>
<body>
...
</body>
</html>What are the merits of meta description tags?
Having meta description tags is crucial because they can be used as snippets by Google for your pages in its search results. However, it's worth noting that Google might choose to use a relevant portion of the visible text on your page if it closely matches a user's query. To ensure that your pages have an informative snippet, it's recommended to include meta description tags on each of your pages.
This way, even if Google can't find a suitable section of text to use in the snippet, your meta description tag will provide a helpful summary. For additional guidance on crafting effective meta descriptions, check out resources.

✅ Accurately summarize the page content
Please provide the original title text or a brief summary of the page's content for me to re-write the title text.
🚫 Avoid :
- Employing a title element that contains text irrelevant to the page's content.
- Resorting to generic or unclear text such as "Untitled" or "New Page 1" in the title element.
✅ Use unique descriptions for each page
Crafting the perfect meta description tag can make all the difference in capturing the attention of potential users. Our team is here to help you write a compelling description that not only informs but also engages and entices searchers to click through to your page.
We understand the importance of conveying all the relevant information users need to decide whether your page will be useful and relevant to them, and we will work with you to ensure that your meta description tag is the perfect representation of your content. Trust us to help your page stand out and drive more traffic to your site.
🚫 Avoid :
- One approach is to use a single meta description tag for all pages or a significant portion of your website's pages.
Use heading tags to emphasize important text
Using Headings to Structure Your Document for Improved Navigation
✅ Imagine you're writing an outline
When preparing content for a webpage, it is helpful to approach it as you would with a significant paper and create a content outline with clear main and sub-points. It is essential to strategically use heading tags to organize and structure your content in a meaningful and logical way.
🚫 Avoid :
- Including content in heading tags that do not contribute to the page's structure or organization.
- Inappropriate use of heading tags instead of more suitable tags such as <em> and <strong>.
- Inconsistent usage of heading tag sizes, leading to disorganized and unclear content structure.
✅ Use headings sparingly across the page
Using appropriate heading tags is crucial for organizing content. However, overuse of heading tags can make it difficult for users to skim through the page and identify the beginning and end of each topic.
🚫 Avoid :
- Overuse of heading tags on a webpage.
- Inclusion of excessively lengthy headings.
- Incorrect use of heading tags solely for text formatting purposes, rather than to indicate structure.
Add structured data markup
Structured data is a type of code that can be incorporated into your website's pages to provide information about your content to search engines. This enables search engines to gain a deeper understanding of the material on your pages and display it in a visually appealing and useful manner in search results. As a result, this can aid in attracting the appropriate type of clients for your company.
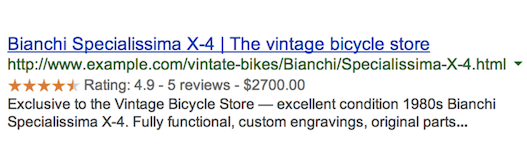
Structured data markup is a powerful tool that can help you enhance your website's search engine visibility and user experience. By marking up individual pages with structured data, you can provide search engines with valuable information about the content on those pages, such as the product type, price, and customer reviews for an online store's product page.
Search engines can use this information to create rich snippets that display key details in search results, which can help attract more clicks and drive more traffic to your website. These enhanced results are known as rich results.
In addition to rich results, structured data markup can also be used to improve the relevance of search results in other formats. For example, if you have a physical store, you can mark up your opening hours to help potential customers find you when you're open and inform them if your store is closed at the time of their search.
Overall, structured data markup is an essential tool for any website owner who wants to improve their website's search engine visibility and provide a better user experience to their visitors.
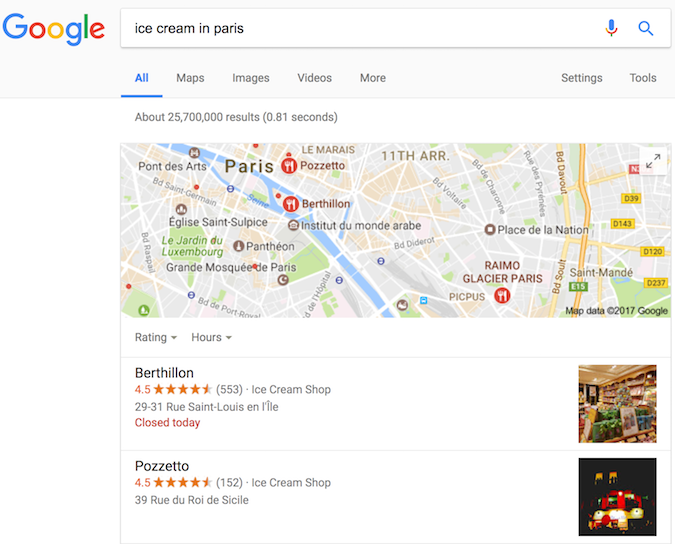
There are numerous business-related entities that can be marked up, including:
- Products that you are offering for sale
- Location(s) of your business
- Videos related to your products or business
- Operating hours of your business
- Listings of upcoming events
- Recipes
- Your company's logo, and much more.
See a full list of supported content types
We suggest utilizing structured data in conjunction with any of the recognized notations markup to depict your content. This can be accomplished by adding the markup to the HTML code on your web pages or by using tools such as Data Highlighter and Markup Helper.
✅ Check your markup using the Rich Results Test
After adding markup to your content, it is important to verify the implementation for any errors using the Google Rich Results test. You can provide either the URL of the content or the HTML code containing the markup.
🚫 Avoid :
- Using invalid markup to ensure the accuracy and effectiveness of the test results..
✅ Use Data Highlighter and Markup Helper
If you're interested in experimenting with structured markup but don't want to modify your site's source code, you can utilize Data Highlighter. It's a feature within Search Console that supports a limited set of content types.
Alternatively, if you prefer to generate the markup code for copying and pasting onto your page, consider using the Markup Helper tool.
🚫 Avoid :
- If you're uncertain about how to implement markup on your website, it's not recommended to modify the source code directly. Instead, it's best to consult with a developer or follow the guidelines provided by the markup language you're working with. Changing the source code without proper understanding may cause errors or unexpected behavior on your site. It's important to ensure that any modifications made to your site's code are done correctly and with a clear understanding of the changes being made.
✅ Keep track of how your marked up pages are doing
In Search Console's different Rich Result reports, you can find information on the number of pages on your website that we've identified with a particular type of markup, their appearance frequency in search results, and the number of clicks they received over the last 90 days. Additionally, any identified errors are displayed.
🚫 Avoid :
- Incorporating markup data that's not visible to users.
- Fabricating reviews or including irrelevant markups.
Manage your appearance in Google Search results
By ensuring that the data on your pages is correctly structured, you can make your page qualify for a variety of special features in Google Search results, such as review stars, decorated results, and others. Take a look at the assortment of search result types that your page can potentially meet the requirements for.
Organize your site hierarchy
Understand how search engines use URLs
To enable search engines to crawl and index content, as well as refer users to it, a unique URL is required for each piece of content. Separate URLs are also needed for different content (such as various products in a shop) and modified content (such as translations or regional variations) to ensure appropriate search results.
Typically, URLs are divided into several distinct sections:
protocol://hostname/path/filename?querystring#fragment
For example:
https://www.example.com/RunningShoes/Womens.htm?size=8#info
In order to ensure website security, Google recommends using https:// whenever possible. The website hostname refers to the location where the website is hosted, often using the same domain name as email. Google distinguishes between the www and non-www versions of the website, such as www.example.com and example.com. When adding your website to Search Console, it is recommended to include both http:// and https:// versions, as well as both www and non-www versions.
The path, filename, and query string are all factors that determine which content is accessed on the server. It is important to note that these three components are case-sensitive, meaning that "FILE" would be interpreted as a different URL than "file." However, the hostname and protocol are case-insensitive, meaning that capitalization does not affect the URL.
A fragment, represented by the "#" symbol (such as #info), typically identifies a specific section of the page that the browser should scroll to. Since the content remains the same regardless of the fragment, search engines usually ignore any fragments used.
When referring to the website's home page, including a trailing slash after the hostname is optional, as it leads to the same content. For the path and filename, however, a trailing slash would be interpreted as a different URL, indicating either a file or directory. For example, https://example.com/fish is not the same as https://example.com/fish/.
Navigation is important for search engines
Website navigation plays a crucial role in facilitating visitors to easily locate their desired content. In addition, it assists search engines in comprehending the significance of the content deemed important by the website owner. Even though Google's search results are page-based, the search engine prefers to grasp the role of a particular page in the overall framework of the site.
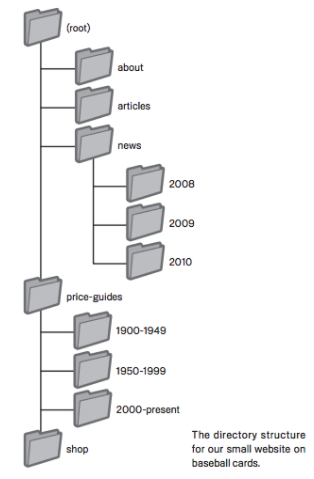
Plan your navigation based on your home page
When planning your website's navigation, start with your home page. As the most frequently visited page on your site, it serves as the starting point for many visitors. Consider how users will navigate from this general page to more specific content. If you have a significant number of pages related to a particular topic, consider creating a dedicated page that lists and describes these related pages. For instance, you might create a structure that goes from the root page to a related topic listing and finally to a specific topic page. Similarly, if you have a large inventory of products, consider organizing them into multiple category and subcategory pages for easy navigation.
Using breadcrumb lists
Breadcrumb navigation is a series of internal links located at the top or bottom of a webpage. Its purpose is to provide visitors with a quick and easy way to navigate back to a previous section or the root page. Typically, the breadcrumb starts with the most general page, usually the root page, on the left, followed by more specific sections to the right. To display breadcrumbs, it is recommended to use breadcrumb structured data markup.
Create a simple navigational page for users
A navigational page is a webpage designed to display the structure of your website, typically featuring a hierarchical listing of all the pages on your site. This page serves as a reference point for visitors who may experience difficulties in locating specific pages on your site. Although search engines also crawl this page, its primary purpose is to aid human visitors. By providing a clear and easy-to-use navigation system, visitors can easily find the information they are searching for on your site.
✅ Create a naturally flowing hierarchy
To help users find specific content on your website easily, incorporate navigation pages into your internal link structure. Ensure that all pages are accessible through links and don't need internal search functionality to be discovered. Include links to related pages to help users discover similar content.
🚫 Avoid :
- Creating intricate networks of navigation links, such as linking every page to every other page on your site.
✅ Use text for navigation
When seeking to facilitate search engine crawling and improve understanding of your site, consider controlling navigation through text links, as this strategy is highly effective. To create a page using JavaScript, incorporate anchor elements with URL values as href attributes and generate all menu items on page-load rather than waiting for user interaction.
🚫 Avoid :
- Relying solely on images or animations for navigation.
- Necessitating the use of script-based event handling to navigate.
✅ Create a navigational page for users, a sitemap for search engines
Create a user-friendly navigation page that contains all the significant pages on your website, or at least the most important ones, if you have a large number of pages. Additionally, produce an XML sitemap file that lists all relevant URLs and their primary content's last modified dates to help search engines find new and updated pages on your site.
🚫 Avoid :
- Allowing broken links to accumulate and not updating your navigational page accordingly.
- Compiling a navigation page that presents pages without proper organization, such as by topic or subject matter.
✅ Show useful 404 pages
It is not uncommon for users to end up on a non-existent page on your website, either due to following a broken link or mistyping a URL. To enhance the user experience, it is recommended to create a custom 404 page that directs them back to a functional page on your site. Consider adding a link to your homepage and providing access to popular or relevant content on your website. To identify the origins of URLs that lead to "not found" errors, you can utilize Google Search Console.
🚫 Avoid :
- Restricting the indexing of your 404 pages on search engines is advisable. This can be achieved by ensuring that your web server returns a 404 HTTP status code or, for JavaScript-based sites, by including the noindex tag whenever non-existent pages are requested.
- Preventing the crawling of 404 pages can be achieved by blocking them through the robots.txt file.
- Providing a non-specific message such as "Not found", "404", or failing to offer a 404 page at all is not recommended.
- Ensure that your 404 pages have a consistent design with the rest of your site.
Simple URLs convey content information
Using descriptive categories and filenames for your website's documents can benefit you in two ways. Firstly, it helps you to organize your site better. Secondly, it creates user-friendly URLs for those who want to link to your content. Visitors may find lengthy and complex URLs with only a few familiar words to be intimidating. This can lead to confusion and a lack of interest in your content. Avoid such URLs and use descriptive categories and filenames to make your site more accessible and appealing to users.
URLs like the following can be confusing and unfriendly:
https://www.brandonsbaseballcards.com/folder1/22447478/x2/14032015.html
If your URL is meaningful, it can be more useful and easily understandable in different contexts:
https://www.brandonsbaseballcards.com/article/ten-rarest-baseball-cards.html
URLs are displayed in search results
Remember that in Google Search results, the URL of a document is typically displayed alongside its title. While Google is capable of crawling through complex URL structures, it is still a good practice to simplify your URLs as much as possible.
✅ Use words in URLs
When it comes to the structure and content of your site, URLs that contain relevant words are more user-friendly for visitors navigating your website.
🚫 Avoid :
- Avoid lengthy URLs that contain unnecessary parameters and session IDs.
- Avoid using generic page names such as page1.html.
- Avoid overusing keywords in your URLs, such as using baseball-cards-baseball-cards-baseballcards.html excessively.
✅ Create a simple directory structure
When organizing your website's content, utilize a directory structure that is intuitive and helps visitors understand their location within the site. Your directory structure should also provide hints about the content found at each URL.
🚫 Avoid :
- Creating excessively nested subdirectories such as .../dir1/dir2/dir3/dir4/dir5/dir6/page.html.
- Using directory names that do not relate to the content contained within them.
✅ Provide one version of a URL to reach a document
When it comes to maintaining the reputation of your content, it's important to ensure that all users are linking to the same URL. Failure to do so may result in the reputation of your content being split between multiple URLs. To prevent this from happening, it's best to focus on using and referencing one URL within your website's structure and internal linking. However, if you do find that the same content is being accessed through multiple URLs, setting up a 301 redirect from the non-preferred URLs to the dominant URL is a great solution. In cases where redirection is not feasible, you can make use of the rel="canonical" link element to achieve the same result.
🚫 Avoid :
- Enabling pages from both the root directory and subdomains to access identical content is achievable, as demonstrated by examples such as domain.com/page.html and sub.domain.com/page.html.
Optimize your content
Make your site interesting and useful
Quality content is the most influential factor in driving traffic to your website. When users encounter compelling and useful information, they tend to share it with others, whether through blog posts, social media, email, forums, or other channels.
Organic or word-of-mouth buzz generated by satisfied users is crucial for establishing your website's reputation with both people and search engines. But without high-quality content, it is difficult to attract and retain visitors who are genuinely interested in what your site has to offer.
Know what your readers want (and give it to them)
When creating content, it's important to consider the keywords that users may use to search for it. Different users may use different search queries depending on their level of knowledge on the topic. To account for these differences in search behavior, it's recommended to use a mix of keyword phrases that anticipate these variations. Google Ads offers a Keyword Planner tool that can help discover new keyword variations and their search volumes. Another useful tool is Google Search Console's Performance Report, which shows the top search queries that led users to your site.
In addition to optimizing content for search, consider offering a unique service that other sites don't provide, conducting original research, breaking exciting news, or leveraging your unique user base. These strategies can help differentiate your site and attract users who may not find the same value on other sites with fewer resources or expertise.
✅ Write easy-to-read text
Users prefer content that is well-crafted and straightforward to comprehend.
🚫 Avoid :
- Producing careless text with numerous spelling and grammar errors.
- Crafting content that is awkward or ineptly written.
- Incorporating text within images and videos for textual content as users may wish to copy and paste the text, and search engines are unable to read it.
✅ Organize your topics clearly
Breaking your content into logical chunks or divisions is always advantageous as it provides visitors with a clear understanding of where one content topic starts and another one ends. This practice also facilitates faster content discovery for users by enabling them to locate the information they need with ease.
🚫 Avoid :
- Presenting an extensive volume of text on diverse subjects onto a page without any organization into paragraphs, subheadings, or distinct layouts.
✅ Create fresh, unique content
Not only will new content retain your current audience, but it will also attract fresh visitors to your website.
🚫 Avoid :
- Replicating (or even plagiarizing) pre-existing material that provides minimal additional benefit to users.
- Possessing indistinguishable or nearly identical variations of your content throughout your website.
Discover additional information about identical content.
✅ Optimize content for your users, not search engines
Focusing on your visitors' needs when designing your website, while also ensuring that it is easily accessible to search engines, typically leads to favorable outcomes.
🚫 Avoid :
- Overstuffing irrelevant keywords solely for the purpose of search engine optimization, often causing frustration or confusion for users.
- Including lengthy segments of text such as "commonly misspelled search queries leading to this webpage" that contribute little substance to user experience.
- Dishonestly concealing content from website visitors while making it visible to search engines.
Act in a way that cultivates user trust
To gain users' trust and make them feel comfortable visiting your site, it's important to establish its trustworthiness. This can be achieved by cultivating a good reputation, particularly in a specific area where you can demonstrate expertise and reliability.
It's also important to provide transparent information about your site, including who publishes it, who provides the content, and what its goals are. If your site involves financial transactions or shopping, make sure to offer clear and comprehensive customer service information to help users address any issues that may arise. Additionally, if you operate a news site, it's crucial to provide clear information about who is responsible for the content.
Finally, it's essential to use appropriate technologies to maintain the security of your site. For example, if your shopping checkout page doesn't have a secure connection, users will not be able to trust the site. Therefore, it's important to prioritize implementing the latest security measures to provide a safe browsing experience for your users.
Make expertise and authoritativeness clear
Ensuring the quality of a website requires an emphasis on expertise and authoritativeness. It is crucial to have content that is created or edited by individuals with relevant knowledge in the topic. Including expert or experienced sources can assist readers in comprehending the content's credibility. When discussing scientific topics, it is advisable to present well-established consensus, if it exists, as a best practice.
Provide an appropriate amount of content for your subject
To produce excellent content, you must invest a considerable amount of time, effort, expertise, and talent/skill in at least one of these areas. It is crucial to ensure that the content is comprehensive, factually accurate, and clearly written. For instance, if your page is about a recipe, it should include a complete recipe that is easy to follow, instead of merely listing the ingredients or providing a basic description of the dish.
🚫 Avoid :
- Insufficient content provided for the intended purpose of the page.
Avoid distracting advertisements
Adverts should be visible on web pages, but they should not be so obtrusive that they detract from the user experience or prevent users from accessing the content they are seeking. This includes adverts that are disruptive, supplementary content, or interstitial pages that make it challenging for users to navigate the website. For further information on this subject, please refer to relevant resources.
🚫 Avoid :
- Placing adverts that are distracting or disruptive on web pages.
Use links wisely
Write good link text
Link text serves as the visible text within a hyperlink. This text conveys information to both users and search engines about the content of the page you are linking to. Links on your webpage can either be internal, directing users to other pages on your site, or external, leading to content on other websites. In both scenarios, the quality of your anchor text plays a crucial role in making it easier for users to navigate and for search engines like Google to comprehend the subject matter of the linked page.
The use of relevant anchor text can greatly enhance the user experience and aid search engines in comprehending the content of linked pages. By providing appropriate anchor text, both users and search engines can quickly and easily understand the topic or subject matter of the page being linked to.
✅ Choose descriptive text
Produce link text that offers a general understanding of the content of the webpage being referenced.
🚫 Avoid :
- Writing generic anchor text like "page", "article", or "click here".
- Using text that is off-topic or has no relation to the content of the page linked to.
- Using the page's URL as the anchor text in most cases, although there are certainly legitimate uses of this, such as promoting or referencing a new website's address.
✅ Write concise text
Write short, descriptive text - a few words or a phrase.
🚫 Avoid :
- Avoid long anchor text.
✅ Format links so they're easy to spot
When creating links, it's crucial to ensure that users can differentiate between regular text and anchor text. If users are unable to spot the links or inadvertently click them, your content loses its effectiveness.
🚫 Avoid :
- Using CSS or text styling that makes links appear identical to regular text.
✅ Think about anchor text for internal links too
Instead of solely focusing on external links, internal linking can also greatly benefit user experience and site navigation. By using clear and relevant anchor text for internal links, both users and Google can better understand the content and structure of your site.
🚫 Avoid :
- Using overly long or keyword-stuffed anchor text that may be designed solely for search engine optimization.
- Creating unnecessary links that do not provide any value to the user's navigation of the site.
Be careful who you link to
The nofollow attribute can be useful in a variety of situations. For instance, when your site links to another site, you may unintentionally confer some of your site's reputation to that site. This can occur when users add links to their own site in your comment sections or message boards. Additionally, if you mention a site in a negative way, you may not want to confer any of your reputation upon it. In such cases, the nofollow attribute can prevent the transfer of reputation.
Another instance where the nofollow attribute can be useful is with widget links. Third-party widgets may contain links that you did not intend to place on your site, and which may have anchor text that you cannot control. If you cannot remove these links from the widget, you can disable them with nofollow. If you create a widget for your own site, it's important to include the nofollow attribute on links in the default code snippet.
Finally, if you want to nofollow all of the links on a page, you can add the tag <meta name="robots" content="nofollow"> to the <head> tag for the page. For more information on robots meta tags, please refer to our documentation.
Combat comment spam with nofollow
To instruct Google that your page should not transfer its authority to the linked pages, assign the rel attribute of a link with a value of nofollow or ugc. The process of nofollowing a link involves inserting rel="nofollow" or a more precise attribute like ugc within the link's anchor tag. Here is an example:
<a href="https://www.example.com" rel="nofollow">Anchor text here</a>
or:
<a href="https://www.example.com" rel="ugc">Anchor text here</a>
In what scenarios is this technique advantageous? Suppose your website features a blog that allows public commenting. Links embedded within such comments may transfer your website's credibility to pages that you might not want to endorse. Comment sections on web pages are often targets for spam comments. Implementing the "nofollow" attribute on user-generated links will prevent your page's reputation from being bestowed upon a spammy site.
If your blogging software does not automatically nofollow user comments, it's important to manually edit them to do so. This applies not only to comments, but also to other parts of your site where users can generate content, such as guest books, forums, shout-boards, and referrer listings. While you may vouch for links added by third parties, such as trusted commenters on your site, it's best to avoid linking to sites that Google considers spammy as this can negatively impact your site's reputation. To prevent comment spam, consider implementing measures such as CAPTCHAs and comment moderation. For more tips, refer to the Google Search Central documentation.
Optimize your images
Use HTML images
✅ Use the HTML <img> or <picture> elements
Use the following HTML elements to embed images in your content:
- <img>
- <picture>
Using semantic HTML markup is crucial in helping crawlers find and process images. Additionally, by utilizing the <picture> element, you can specify multiple options for different screen sizes to ensure that your images are responsive. Furthermore, using the loading="lazy" attribute on images can enhance your page's loading speed, resulting in a better user experience.
🚫 Avoid :
- Using CSS to display images that you want to index.
Use the alt attribute
What is the purpose of using the alt attribute? The alt attribute serves as a source of information about pictures for users who access your site with assistive technologies, such as screen readers.
In addition, if an image is used as a link, the alt text is treated as the anchor text of a text link. However, it's not advisable to rely too heavily on images for links in your site's navigation when text links could fulfill the same function. Lastly, optimizing your image filenames and alt text can improve the ability of image search engines like Google Images to accurately interpret your images.
✅ Use brief but descriptive filenames and alt text
Similar to other page elements targeted for optimization, filenames and alt text should be concise yet descriptive.
🚫 Avoid:
- Use generic filenames such as "image1.jpg," "pic.gif," or "1.jpg" if possible. If your site contains a large number of images, you may want to consider automating the naming of images.
- Create overly long filenames.
- Overload alt text with keywords or copy and paste entire sentences.
✅ Supply alt text when using images as links
When utilizing an image as a link, ensure that you provide descriptive alt text to aid Google in comprehending the linked page's content. Approach it as you would when composing anchor text for a text link.
🚫 Avoid:
- Craft long and spammy alt text.
- Depend solely on image links for your website's navigation.
Help search engines find your images
Similar to the XML sitemap file for your web pages, an Image sitemap can offer Google additional details regarding the images discovered on your website. As a result, the probability of your images appearing in Google Images results is increased. The organization of this document is comparable to that of the XML sitemap file.
Use standard image formats
Use image file formats that are widely supported by browsers, such as JPEG, GIF, PNG, BMP, and WebP. Additionally, it's recommended that you match the file extension of your filename with the actual file type to ensure compatibility.
Make your site mobile-friendly
In today's world, mobility is paramount. The majority of individuals are utilizing a mobile device to conduct searches on Google. However, the desktop iteration of a website may be inconvenient to navigate and utilize on a mobile device. Therefore, it is essential to have a website that is optimized for mobile usage in order to maintain a strong online presence. Moreover, starting in the latter half of 2016, Google began experimenting with utilizing primarily the mobile version of a website's content for generating snippets, parsing structured data, and determining search rankings.
Understand the difference between devices
- Smartphone - For the purposes of this document, the term "mobile" or "mobile devices" specifically refers to smartphones running operating systems such as Android, iPhone, or Windows Phone. Despite having smaller screens, mobile browsers are capable of rendering a broad range of the HTML5 specification, much like desktop browsers. However, their default orientation is almost always vertical.
- Tablet - Tablets are generally considered to be a distinct class of device, and are not typically included in the definition of mobile devices for the purposes of this document. Tablets generally have larger screens, which means that unless your site offers optimized content specifically for tablets, users are likely to expect a desktop-like browsing experience rather than one tailored to smartphone browsers.
- Multimedia phone - Multimedia phones are equipped with browsers that are capable of rendering pages coded to meet XHTML standards, support HTML5 Markup, and JavaScript/ECMAScript. However, they may not support some of the extension APIs found in the HTML5 standard. This describes the browser found in most 3G-ready phones that are not smartphones.
- Feature phones - Browsers on feature phones lack the ability to render normal desktop web pages coded using standard HTML. This includes browsers that render only cHTML (iMode), WML, XHTML-MP, and similar technologies.
While our recommendations primarily focus on smartphones, we encourage site owners with multimedia and feature phones to follow the same advice whenever appropriate.
Choose a mobile strategy
Google supports various methods for making your website mobile-ready, including:
- Responsive web design (Recommended)
- Dynamic serving
- Separate URLs
To check if your site meets Google's criteria for mobile-friendliness on search result pages, you can use the Mobile-Friendly Test. You can also use the Mobile Usability report in Search Console to identify and fix any mobile usability issues on your site.
If your site contains a lot of static content spread across multiple pages, consider implementing AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages). AMP is a specialized version of HTML that ensures fast and user-friendly site performance, and can be further optimized for speed by various platforms, including Google Search.
Configure mobile sites so that they can be indexed accurately
When setting up your mobile site, it's important to keep in mind the following key points:
- Signal to Google when a page is mobile-friendly or has an equivalent mobile version. This is particularly important if you're using Dynamic Serving or have a separate mobile site, as it helps Google accurately serve your content to mobile searchers.
- If you're using Responsive Web Design, use the
meta name="viewport"tag to tell the browser how to adjust the content. If you're using Dynamic Serving, use the Vary HTTP header to signal changes depending on the user agent. If you're using separate URLs, use the<link>tag withrel="canonical"andrel="alternate"elements to signal the relationship between two URLs. - Keep all resources crawlable. If Google doesn't have access to a page's resources, it may not detect that it's mobile-friendly and may not properly serve it to mobile searchers. Avoid blocking page resources, such as CSS, JavaScript, or images, through your robots.txt file.
- Avoid frustrating mobile visitors by eliminating common mistakes, such as featuring unplayable videos or using full-page interstitials on mobile that hinder user experience. Google may demote pages that provide a poor searcher experience in mobile search results.
- Provide full functionality on all devices, including mobile. Make sure that all important images, videos, and textual content are embedded and accessible on mobile devices. Provide all structured data, metadata, and other meta-tags on all versions of your pages for search engines.
- Ensure that the structured data, images, videos, and metadata on your desktop site are also included on the mobile site. This helps Google better understand your content and serve it to mobile searchers accurately.
Best Practices
- To check if your website functions properly on mobile devices, utilize the Mobile-Friendly Test provided by Google.
- If you have separate URLs for your mobile and desktop pages, it's important to test both versions to ensure that the redirect is recognized and can be crawled.
For further details, refer to Google's guide on mobile-friendly design.
Promote your website
To ensure that others discover the hard work you've put into your content, it's important to effectively promote it. Although most links to your site will be added gradually as people find and link to it, you can take steps to speed up the process. However, it's essential to be cautious as going overboard can damage your site's reputation.
One effective way to promote new content or services is by creating a blog post on your site to inform your audience. This will increase visibility, and other website owners may also share your story if they follow your site or RSS feed.
In addition to online efforts, offline promotion can also be rewarding. For instance, if you own a business site, make sure its URL is displayed on your business cards, letterhead, posters, and other marketing materials. Furthermore, consider sending regular newsletters via mail to keep clients informed about new content on your site.
If you own a local business, claiming your Business Profile can help you connect with potential customers on Google Maps and Google Search.
Know about social media sites
Instead of constantly promoting small pieces of content, focus on creating and sharing larger, more engaging content that will attract and retain interested groups of people.
🚫 Avoid :
- Participating in schemes that artificially promote your content to the top of sharing services. Instead, focus on building a site that encourages user interaction and sharing, which will organically lead to your content being matched with interested groups of people.
Reach out to those in your site's related community
Likely, there exist various websites that delve into subject matters akin to yours. It can be advantageous to establish a line of communication with these sites. Discussions pertaining to the trending topics within your niche or community can serve as inspiration for generating fresh content or developing a valuable resource for your community.
It's best to steer clear of Also, refrain from buying links from another site with the sole intent of boosting your PageRank.
🚫 Avoid :
- Refrain from buying links from another site with the sole intent of boosting your PageRank.
- Spamming other sites with requests for backlinks that relate to your topic area.
Analyze your search performance and user behavior
Analyzing your search performance
Google, among other major search engines, provides website owners with tools to evaluate their search engine performance. Google's tool, known as Search Console, offers two essential categories of information: whether Google can find your content and how your website is performing in Google Search results.
Using Search Console will not provide your site with preferential treatment, but it can help you identify issues that, if fixed, can improve your website's performance in search results. With this service, website owners can:
- Determine which parts of their site Googlebot had trouble crawling
- Test and submit sitemaps
- Generate or analyze robots.txt files
- Remove URLs already crawled by Googlebot
- Specify a preferred domain
- Identify issues with
titleanddescriptionmetatags - Understand the top searches used to reach their site
- Gain insight into how Google perceives their pages
- Receive notifications of spam policy violations and request a site reconsideration
In addition to Google's Search Console, Microsoft's Bing Webmaster Tools also provides tools for website owners.
Analyzing user behavior on your site
If you have made improvements to the crawling and indexing of your website through services like Google Search Console, you may be interested in tracking the traffic to your site. Web analytics programs, such as Google Analytics, can provide valuable insights for this purpose. They allow you to:
- Gain an understanding of how users arrive at and engage with your website.
- Identify the most popular content on your website.
- Evaluate the impact of optimizations made to your site, such as changes to title and description meta tags, to determine if they have increased traffic from search engines.
For advanced users, combining the information provided by an analytics package with data from server log files can offer even more comprehensive information about how visitors interact with your documents. This includes additional keywords that searchers may use to find your site.
Additional Resources
Google Search Central blog: Stay up-to-date with the latest information on Google Search updates, new Search Console features, and more by following our Google Search Central blog.
- Google Search Central blog: Get answers to your website-related questions and discover tips for creating high-quality sites from experienced contributors, including Product Experts and Googlers, in our product forum for website owners.
- Google Search Central Twitter: Follow us on Twitter for news and resources that can help you create an outstanding website.
- Google Search Central YouTube Channel: Watch hundreds of helpful videos that are specifically created for the website owner community and have your questions answered by Googlers.
- How Search Works: Gain insights into what happens behind the scenes as you search for something on Google Search.


