Redirect chains can often be a source of frustration for website owners and visitors alike. Understanding the concept of redirect chains is essential for efficiently addressing this issue.
Understanding the Concept of Redirect Chains
To effectively fix redirect chains, it's crucial to comprehend what they are. A redirect chain occurs when a URL points to another URL, which in turn redirects to a third URL, and so on.
These chains can consist of multiple redirections in a sequence before arriving at the final destination. This can slow down the loading time of your website and negatively impact user experience.
To illustrate, let's say a user clicks on a link to your website, but that link redirects them to another URL, which then redirects them again before finally reaching your desired webpage. This multi-step process can be problematic because each redirection adds extra time to the page load, potentially leading to user frustration.
The Negative Impact of Redirect Chains
Redirect chains can have a significant detrimental effect on your website's performance and user experience. Let's explore why they are bad for SEO and examine some real-world examples of redirect chain issues.
Why are redirect chains bad for SEO?
Redirect chains are detrimental to your website's search engine optimization (SEO) efforts for several reasons. Firstly, they can lead to a loss of link juice, which refers to the value or authority passed from one page to another through hyperlinks. When a redirect chain is in place, it dilutes the link equity, potentially impacting the ranking power of the final destination URL.
Secondly, redirect chains can severely reduce your site's performance. Every additional redirect adds a layer of complexity, resulting in longer loading times. Slow-loading pages are frustrating for users and can lead to high bounce rates, which in turn can negatively impact your search engine rankings.
Lastly, from a search engine's perspective, dealing with redirect chains can present crawling concerns. Search engine bots may struggle to navigate through these multiple redirects, leading to incomplete indexing and potential SEO issues.
Examples of redirect chain issues:
Link Juice Loss
Imagine a scenario where your website has multiple pages linked to one another. If a redirect chain is present, the link equity from these pages gets diluted with each additional redirect. The final destination page receives less authority, impacting its ability to rank well in search engine results.

Reduced Site Performance
Redirect chains introduce unnecessary delays in page loading. As a result, users experience slower load times, which can deter them from exploring your website further and even lead to higher bounce rates. Slow-loading pages can negatively impact your SEO efforts and user satisfaction.
Crawling Concerns
Search engine crawlers aim to index your website effectively. When they encounter redirect chains, it complicates their journey. Excessive redirects can confuse the bots, leading to incomplete indexing, missed content, and potential SEO issues. It's crucial to provide a clear and efficient path for search engine crawlers to navigate your site.
Comparing Redirect Chains and Redirect Loops
Redirect chains and redirect loops are both issues that can impact your website's performance and user experience. Let's delve into the distinctions between these two redirection problems and explore the crucial differences.
What is the difference between redirect chains and loops?
Redirect chains and redirect loops are similar in that they involve multiple redirections, but they differ in how those redirections occur.
A redirect chain is a series of consecutive redirects where one URL points to another URL, which then redirects to a third URL, and so on. Each step in the chain represents a separate HTTP request and adds to the loading time of a page.
On the other hand, a redirect loop occurs when two or more URLs continuously redirect to each other in a never-ending cycle. For example, URL A redirects to URL B, which in turn redirects back to URL A. This loop can cause a page to load indefinitely, which is highly problematic for both user experience and SEO.
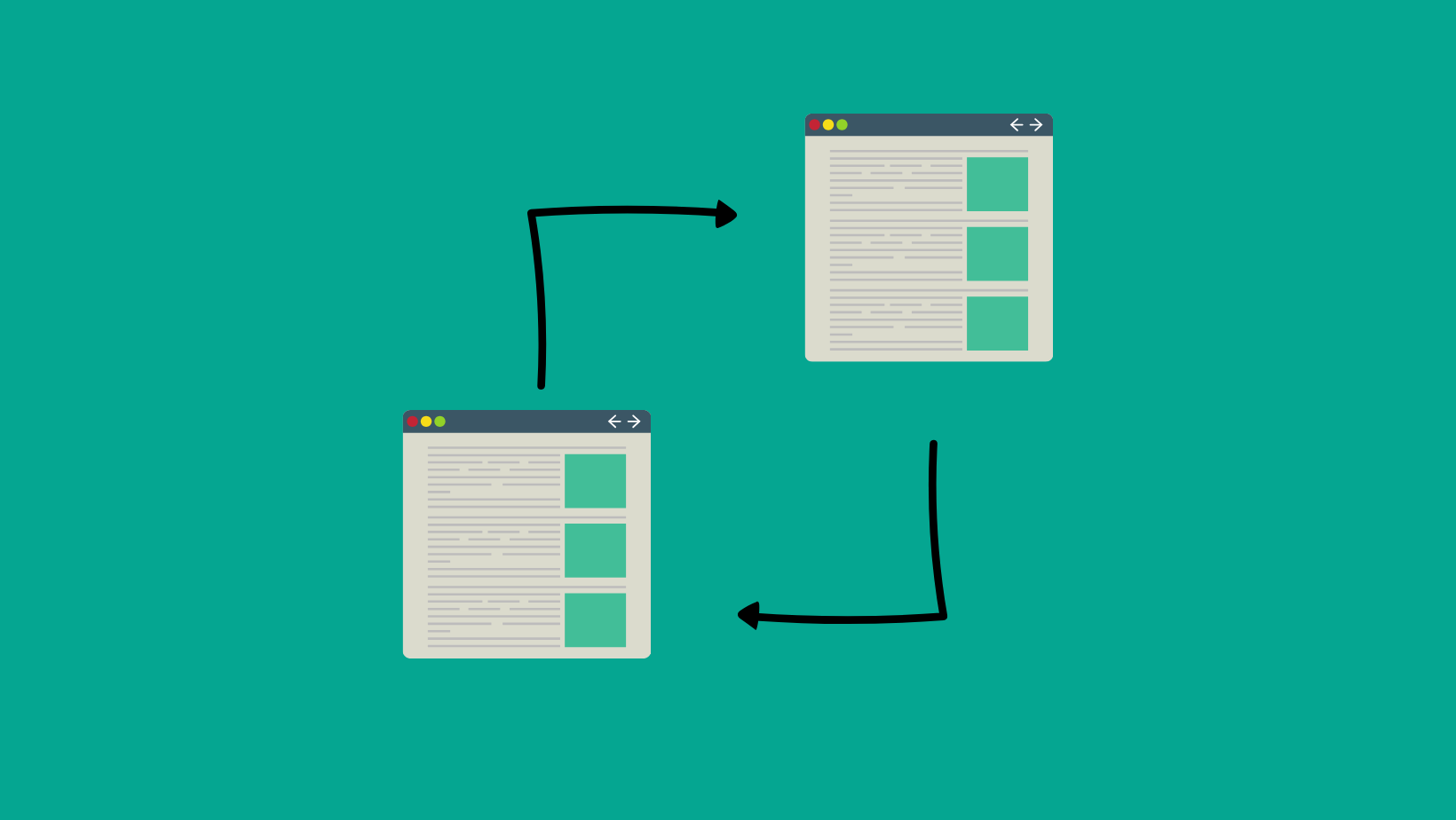
Redirect chains vs redirect loops
When comparing redirect chains and loops, it's essential to understand their distinct characteristics and the impact they have on your website.
Redirect chains are more common and generally easier to identify. They can affect your website's performance by adding delays to page loading, reducing link equity, and causing crawling issues. While redirect chains are problematic, they are usually straightforward to fix by removing unnecessary redirects and streamlining the path to the final destination URL.
Redirect loops, on the other hand, are a more severe issue as they can result in a never-ending cycle of redirection, leading to an infinite loading loop for users. This can be frustrating and detrimental to your site's SEO and reputation. Detecting and resolving redirect loops requires careful analysis and correction of the URLs involved to break the cycle and ensure a smooth user experience.
How Redirect Chains are Created
Redirect chains are a common issue that can have a significant impact on your website's performance. To effectively address and fix redirect chains, it's essential to understand how they are created and the common scenarios that lead to their formation.
How Do Redirect Chains Happen?
Redirect chains occur when multiple redirections are in place, causing a single URL to pass through several intermediary steps before reaching its final destination. These chains are typically created in the following ways:
Content Has Moved: When you update the structure or location of your website's content, such as changing the URL of a page or moving content to a different directory, you might implement redirection to guide users to the new location. However, if not done correctly, it can lead to redirect chains. This often happens when older URLs are redirected to new ones, which are themselves subject to further redirections.
Domain Migration: When you change your website's domain name, it often involves setting up redirects from the old domain to the new one. If not configured properly, these redirections can form chains, as users are redirected from the old domain to an intermediary URL and then to the final destination on the new domain.
Understanding the root causes of redirect chains is crucial for preventing them in the first place. Now, let's look at some examples of scenarios where redirect chains can become problematic.
Examples of Content Has Moved and Domain Migration
Content Has Moved: Imagine you decide to restructure your website, and as a result, you change the URL of a specific page. To ensure a seamless user experience, you set up a redirect from the old URL to the new one. However, if you later decide to change the new URL again or redirect it to a different location, this can create a chain of redirects. The user is initially redirected from the old URL to the first new URL and then from there to the second new URL, creating a redirect chain.
Domain Migration: In the case of domain migration, if you change your website's domain name, you'll often establish redirects from the old domain to the new one. However, if you configure these redirects incorrectly, visitors may encounter a chain of redirections. They start on the old domain, get redirected to an intermediary URL, and then finally reach the new domain. This sequence can lead to slow page loading times and negatively affect user experience.
Identifying these scenarios and understanding how redirect chains are formed is the first step towards effectively resolving them and optimizing your website's performance.

Tools to Check Redirect Chains and Loops
To effectively address and fix redirect chains on your website, you need the right tools to identify and analyze these issues. Let's explore how you can determine the presence of a redirect chain and the tools available for checking and resolving them.
How can you see if there is a redirect chain?
Detecting a redirect chain is essential before you can fix it. To check for the presence of a redirect chain, follow these steps:
Manually Check Redirects
You can start by manually navigating through your website and monitoring the URL changes in the address bar. If you notice that a single URL leads to multiple intermediary redirects before reaching the final destination, you likely have a redirect chain.
Use Browser Developer Tools
Modern web browsers provide developer tools that allow you to inspect network activity. Open your browser's developer tools, go to the "Network" tab, and initiate a request to the URL in question. You'll see the sequence of HTTP requests and redirects. If multiple requests are made before arriving at the destination URL, it's a sign of a redirect chain.
Tools for checking redirect chains:
Redirect-checker.org
Redirect-checker.org is a user-friendly online tool that enables you to check for redirect chains and loops by simply entering a URL. It provides a detailed report of the redirection path, making it easy to identify the issue and take appropriate action.
Sitebulb
Sitebulb is an advanced website auditing tool that offers in-depth analysis of your site's structure, including redirect chains. It provides comprehensive reports and insights, helping you pinpoint and address redirection issues effectively.
Also see: Sitebulb SEO Product Tour, Reviews & More 2023

Screaming Frog
Screaming Frog is a powerful SEO spider tool that can crawl your website and uncover various SEO-related issues, including redirect chains. It offers detailed reports, making it an excellent choice for comprehensive website analysis.
Also see: Screamingfrog SEO Product Tour, Reviews & More 2023
Lumar - formerly known as DeepCrawl
Lumar, or DeepCrawl, is another professional website crawler that assists in identifying redirect chains, among other SEO concerns. It provides insights into your site's structure and helps you understand and rectify redirection problems.
Also see: Deepcrawl SEO Product Tour, Reviews & More
These tools simplify the process of identifying and resolving redirect chains and loops on your website, ensuring a smoother user experience and better SEO performance.
How to Find and Fix Redirect Chains Step by Step
Redirect chains can be a headache, but fear not, as we have a step-by-step guide to help you find and fix them. Let's dive into the process of resolving redirect chain issues.
How do I fix a redirect chain?
Fixing a redirect chain involves a series of steps, from identifying the issue to implementing the necessary changes. Here's a breakdown of the process:
Step #1 – How to find redirect chains
- Manual Inspection: Alternatively, you can manually navigate your website and keep an eye on the address bar as you move from page to page. If you notice multiple intermediary redirects before reaching the final destination URL, you've likely found a redirect chain.
Step #2 – How to properly set up redirects for SEO
Once you've identified the redirect chains on your site, it's time to take action and ensure proper setup for SEO-friendly redirects:
- Proper HTTP Status Codes: Ensure that the HTTP status codes are correctly set for your redirects. Use 301 (Permanent Redirect) for pages that have permanently moved, and 302 (Temporary Redirect) for temporary changes. This helps search engines understand the intent of your redirects.
- Update Internal Links: Go through your website's internal links and ensure they point directly to the final destination rather than intermediate pages in the chain.

Step #3 – Setting up Redirects in WordPress
If your website is built on WordPress, setting up redirects can be accomplished through the use of plugins.
1. Install a Redirect Plugin: Search for and install a reliable WordPress redirect plugin, such as "Redirection" or "Yoast SEO."
2. Configure Redirections: Access the plugin's settings and configure the necessary redirects. You can specify the source URL, the target URL, and the redirection type (e.g., 301 or 302).
3. Test and Monitor: After setting up redirects, thoroughly test your website to ensure the redirections are working as intended. Monitor your site for any new redirect chain issues that may arise.
By following these steps, you can efficiently find and fix redirect chains, improving your website's SEO and providing a better user experience for your visitors.
Preventing Redirect Chains
Redirect chains can be a hassle to fix, but taking steps to prevent them in the first place is even more valuable. Let's explore the reasons behind redirects, how to minimize redirect chains and strategies for preventing them on your website.
Two Reasons for Redirects
Redirects are typically implemented for two main reasons:
Content or URL Changes: When you make changes to your website's content, such as altering the URL structure, merging or deleting pages, or reorganizing your site, you may need to set up redirects. This ensures that visitors and search engines can still access the updated or relocated content.
Domain Changes: Domain migration is another common reason for redirects. When you change your website's domain name, it's crucial to set up redirects from the old domain to the new one. This helps in preserving your site's SEO value and ensuring that users reach the correct destination.

How can you minimize redirect chains?
Minimizing redirect chains starts with a proactive approach:
Plan URL Changes Carefully: Before making significant changes to your website, plan them thoughtfully. Consider the impact on URLs and how the changes will affect the structure. Avoid excessive changes that lead to redirect chains.
Update Internal Links: Whenever you make updates to your site's content or URLs, ensure that internal links are also updated to reflect the changes. This prevents the need for additional redirects.
Use Relative Links: Instead of using absolute URLs, use relative links when linking to pages within your own site. Relative links are less likely to result in redirect chains when content moves.
Regularly Audit Your Site: Conduct regular audits of your website's structure and redirects. Identify and fix any emerging redirect chains promptly.
How to Prevent Redirect Chains
Implement Proper URL Redirects: When implementing redirects, make sure they are set up correctly from the start. Use 301 redirects for permanent changes and 302 redirects for temporary alterations.
Monitor Your Site: Regularly monitor your website for any unexpected or unintended redirects. Address these issues promptly to prevent the formation of redirect chains.
Educate Your Team: If multiple individuals work on your website, ensure that they are aware of the importance of proper redirect management and the potential consequences of redirect chains.
By taking a proactive approach, understanding the reasons behind redirects, and following best practices, you can effectively minimize and prevent redirect chains on your website. This not only improves user experience but also enhances your site's SEO performance.
Conclusion
Fixing redirect chains is a crucial aspect of maintaining a well-performing website and ensuring a positive user experience. In this article, we've delved into the intricacies of redirect chains, from understanding their impact on SEO to finding, fixing, and preventing them.
By identifying the root causes of redirect chains, utilizing the right tools, and following a step-by-step process, you can efficiently resolve these issues and enhance your website's overall performance. Furthermore, we've emphasized the significance of preventing redirect chains through careful planning, updating internal links, and maintaining vigilance.
Remember that addressing redirect chains not only benefits your SEO efforts but also contributes to a smoother and more satisfying user experience. As you work to fix existing redirect chains and prevent new ones from forming, you're on the path to a more efficient, user-friendly, and search-engine-optimized website.

